Core Competencies At Work
How is it that some companies continue to be successful and innovative for years, even decades? In any field, this is a challenge, and even more so with the rapidly changing technology landscape. Companies that excel across decades can do this because they successfully implement cultures and philosophies that breed innovation and an awareness of market trends. This happens purposely as a result of how the organization and its’ individuals act.
One way of doing this is by developing core competencies. Competency management for individuals refers to defining the necessary skills required to perform successfully to a set of criteria, such as an employee’s role. And at a macro level, core competencies are defined as “strategic advantages of a business, including the combination of pooled knowledge and technical capacities, that allow it to be competitive in the marketplace,” according to Investopedia. Having a few central themes and behavior sets help direct organizational decisions.
Learn MoreBelow I’ve highlighted Google, Amazon, and Facebook, outlined common themes that allow them to be innovative, and summarized them so you can begin to implement them as core competencies within your own organization.
Google: Organizing the World’s Information

Google is a company that is synonymous with search, and as a result, information. Google is the world’s search engine leader, with over 63% of U.S. searches conducted on the platform, which accounts for 84% of its total revenue.
Google is one of the world’s most innovative companies because it does not stop at just delivering the world’s most popular search engine, but in carrying this mission of democratizing the world’s information through many other methods. These include platforms that today are commonplace such as Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Earth, to futuristic missions such as driverless cars, and delivering internet to the more than three billion people who still do not have access.
Google can remain innovative and successful because of its reliance on several core competencies, such as:
- Flexible
- Open Source Mentality
- Think Big
Flexible Structure Produces More Innovation
The organization is famous for building change and innovation into the company from the ground up with its creative structure. One example of this is with its “20% time” model, which allows employees one full day a week to work on any project they choose.
While not always productive or effective (ex-Googler Marissa Mayer says it’s really “120% time”), the policy has led to some of Google’s most popular products including:
- Gmail
- Google Cardboard
- Google News
- Google Earth
Google builds innovation and changes into the company’s culture with policies and encouragement. In a 2016 talk at the Forbes CIO Summit, Google CIO Ben Fried even mentioned that change is one of its most important core competencies, saying, “People are creatures of habit, and yet technology has never moved as quickly as it is today. As a result, CIOs need to make change a core competency. The ability to change is essential to stay competitive.”
Google has even upped the ante on its dedication to change with its in-house incubator Area 120. According to Fast Company, this idea was instituted two years ago, and is similar to 20% time, with one major difference – employees who are selected spend 100% of their time on the project. Google can behave like a startup with the resources of a major corporate company in this way.
Sourcing the Best Ideas from All

With such divergent products and services, from a search engine to driverless cars, to Android phones, Google is a huge proponent of the “open-source mentality” that many developers have. The company welcomes research and insight from many types of people and disciplines, whether they are in the company or not.
According to Inc.com, Google greenlights over 250 new research projects a year, spending billions of dollars in the process, and even inviting researchers on-site for their sabbaticals. The company has a history of acquiring or investing in seemingly unrelated companies due to scientific or data capabilities. Examples include Nest, the thermostat and smart home company it acquired for $3.2 billion, or 23andMe, the company that can sequence anyone’s genome, in which Google invested millions of dollars.
Google welcomes all types of researchers to access its tools, data, and knowledge in order to make discoveries. And in the truest sense of the word, Google’s wildly successful Android operating system is fully open source. It’s worth noting that Android phones account for over 80% of all phones sold.
Thinking Big (and Backing it Up!)
With so many ambitious projects that Google has produced or is currently working on, it’s no secret that the company likes to think big. But just thinking is not enough, the company backs this up with its actions, and segments the organization in ways that allow its best big thinkers to do what they do best.
Google underwent a huge structural change in 2015, repurposing the company so that its core services (such as search and AdWords) were under the Google umbrella, but its more diverse projects were under different companies.
The overarching parent company is called Alphabet, which owns Google as well as several other companies, all of which report to Larry Page, one of the co-founders of Google.
This is a big deal because it allows Alphabet to make longer-term bets with its other wings of the organization while continuing its core products/services.
One of the most secretive of these new companies is entitled simply “X” and has also been called “The Moonshot Factory” according to the company’s website. This takes the evolution of 20% time and Area 120 to an even greater level. Some of the exciting new projects that are a part of X include:
- Waymo: A self-driving car project.
- Wing: A delivery drone service.
- Loon: A project to create worldwide internet access using balloons.
- Malta: A project to store renewable energy in molten salt.
- Brain: A research project on Artificial Intelligence and machine learning.
This is just a fraction of the ambitious projects Alphabet, Google, and X have in the pipeline, which sums up Google’s core competencies in a nutshell. As Managing Director of Area 120, Alex Gawley says, “You want to build products that solve problems that people encounter daily.” Google can do this consistently because of the core competencies it has developed and deliberately built into the culture of its organization.
Learn MoreAmazon: A Customer-Centric Company

It’s no secret that Amazon has become an incredibly successful and omnipresent company in the marketplace; the organization is currently listed as the second most valuable in the world.
The company has not only been able to grow its core business as an e-commerce giant but has been able to innovate and move into other market segments successfully. While Amazon does many things well, some of its most significant core competencies are:
- Distribution and Logistics
- Creating Self-Sustaining Platforms
- Leveraging Technology
Distribution and Logistics Core Competency

Amazon thinks of itself as “Earth’s most customer-centric company” according to its website’s mission statement. It delivers on this mission with an unparalleled ability to streamline the buying process, deliver products quickly and efficiently, and create tools and an ecosystem where vendors and customers can connect with each other.
The company changed the e-commerce landscape with the introduction of Amazon Prime and guaranteed two-day shipping back in 2005. And it went even further with the introduction of Prime Now in 2015, guaranteeing delivery within two hours for select products and in select cities. This type of distribution capability is unmatched by other organizations.
Creating Closed Ecosystems
But Amazon thinks differently, and not only wants to provide products to the globe, but to provide tools and platforms for others to create and run their businesses. In this way it executes on another competency, creating closed ecosystems and platforms for sellers. On Amazon.com in 2017, over half of all sales were by third-party merchants, according to a shareholder’s letter by CEO Jeff Bezos. And not only that, but 55% of online shoppers begin their product search on Amazon, according to a 2016 survey from BloomReach.
With such a high volume of businesses succeeding on Amazon, the company ensures that not only will it continue to earn fees from these companies, but that they will stay on the platform because they are making money!
The company continues to innovate with this way of thinking, providing multitudes of platforms that allow sellers, content creators, and more to distribute products and services under the Amazon umbrella. Here are just a few examples:
Twitch – Video Game Streaming
Twitch is a massive force in the video game industry and streaming in general. One of the most popular broadcasters is a 26-year-old who goes by the name Ninja and makes an estimated $350,000 each month from the platform. He was recently joined by popular rapper Drake during a Fortnite game, smashing Twitch’s record and resulting in 628,000 concurrent streams. Twitch is growing in popularity fast and will become a platform that many aspiring gamers build their careers on.
Audible – Audiobooks
In a totally different market, Amazon has also become the go-to platform. According to Observer, 44% of audiobooks are purchased on Audible.com, which Amazon owns. Audiobooks are growing in popularity, increasing sales by 20% in 2017. Audible is not only the place people go to listen to audiobooks, it’s where many independent authors sell their books and depend on the platform for their careers as well.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Cloud Hosting
Amazon made a big early bet with its cloud computing network, Amazon Web Services. AWS now hosts over 33% of the cloud and is Amazon’s fastest-growing business, growing 252% in the past three years. While competitors such as Google’s Cloud service and Microsoft Azure are growing too, Amazon has a big lead. Amazon has positioned itself so that it hosts much of the world’s internet. Not only do independent streamers, authors, and small businesses depend on Amazon’s platforms, a huge organization, such as Netflix, Spotify, Airbnb, Comcast, and more host platforms using Amazon Web Services.
Whole Foods – Supermarket Chain
And lastly, while Amazon’s dominance on the web is clear, it is worth noting that the company is making strategic acquisitions to establish itself offline too. With its purchase of Whole Foods in 2017, the company now sells the food you eat as well.
Amazon’s vision is to create closed, interwoven ecosystems of buying and selling. Many people now and in the future will buy most products on Amazon.com, buy groceries from Whole Foods, host their website on AWS, and use Amazon’s eCommerce platform for their business. Amazon understands the virtuous cycle that occurs as more and more commerce platforms are interconnected and owned by the organization.
Leveraging Technology for the Future

Of course, none of this is possible without reliance on sophisticated technology and a constant push to improve it. Amazon has its hands in many divergent markets, but with all of them, it brings its signatures of unparalleled customer convenience and forward-thinking technology.
Amazon can innovate quickly and consistently because it practices an agile methodology, a common approach to software code writing, and applies this to the organization at large. It focuses on creating small teams quickly and producing a minimum viable product as fast as possible. The organization prioritizes “launching early over everything else,” according to a former employee memo.
One example of Amazon leveraging technology in a disruptive way is its own version of a convenience store, called Amazon Go. These cashier-less stores have high-tech cameras that record what customers choose, and then charge digital carts as people walk out of the store.
Examples of leveraging technology can also be seen in its use of drones and robot workers to help improve the efficiency of its e-commerce business. The company currently uses robots in its warehouses to help with moving inventory and has plans to deliver to customers’ doorsteps using drone technology.
Amazon constantly delivers on its mission of being “Earth’s most customer-friendly company” due to a consistent reliance on core competencies such as distribution, logistics, creating platforms and tools for people, and leveraging technology.
Learn MoreFacebook: Making the World More Connected

(Image Source: Facebook)
One of Facebook’s core competencies is the ability to rapidly iterate and add new features; it was named one of Fast Company’s most innovative companies of 2017. According to the article, Facebook innovated with concepts such as “the Creative Hub, a platform for businesses and agencies to mock up, share, and test ads.” It has several core competencies that permeate the entire company and allow them to be consistently innovative. These include:
- Move Fast
- Employee Autonomy
- Focus on Impact
Move Fast and Break Things
Facebook likes to exemplify the Silicon Valley mantra “Move Fast and Break Things” which is the hacker’s mentality. In Mark Zuckerberg’s 2012 letter to investors, he said, “Hackers try to build the best services over the long term by quickly releasing and learning from smaller iterations rather than trying to get everything right all at once.”
This agile approach can come with its fair share of difficulties. Facebook has faced plenty of backlash with controversies lately, including a major data security breach that led to Zuckerberg testifying before congress. But this willingness to be bold and fast-moving has its benefits. Facebook consistently creates products and improvements to its platform quickly. Significant features such as removing trending topics, adding timeline stories, and adding image filters have all been launched in the past few years. The “hacker way” allows the company to move quickly and constantly improve the platform.
Give Employees Trust
Facebook also notably gives its employees autonomy and trust, and with that comes self-imposed high standards of responsibility and performance. In an article written by a former employee Pedram Keyani, he tells a story about working on a code change to the Timeline which was pushed out to 25 million people on his second day at the company.
Zuckerberg himself echoed this also in the investor letter, saying that the developers organize hackathons on their own, and that “Many of our most successful products came out of hackathons, including Timeline, chat, video, our mobile development framework, and some of our most important infrastructure…”
Facebook can make innovation a daily habit with these principles. According to Spigit, which provides innovation management software, idea frequency, implementation, and executive buy-in are crucial. These are three principles Facebook holds. Not only do the employees self-organize and enjoy the process of creating new products, but executives including Zuckerberg himself, get involved and implement the best ideas that stem from these sessions. This motivates employees to continue thinking outside the box.
Focus on Impact
And lastly, Facebook can innovate and be successful because it operates based on a shared goal of changing the world for the better. The company’s mission is to “make the world more open and connected,” and this inspires employees to create great products and services. This philosophy drives all company actions, whether operational decisions, or hiring, and allows the organization to be consistently competent and high-performing. Facebook is listed every year as one of Glassdoor’s best companies to work for this very reason. The employees believe in Facebook’s mission and are inspired to go to work every day.
Innovate in Your Organization by Bringing These Core Competencies Together

There are many similarities between these three organizations and others that are top-performing. For those that want to focus on innovation, there are some common themes to follow:
- Foster a Culture of Innovation.
- Be open to new ideas and open communication with executives.
- Trust employees and give them freedom.
- Move quickly and look for the next improvement always.
- Don’t be afraid to fail.
- Have a higher purpose.
Foster a Culture of Innovation
While it may seem obvious, being an innovative company does not happen accidentally, but by deliberately setting the company up for this type of success. Google, Amazon, and Facebook all have different ways of accomplishing this, but all have the type of structure that allows them to innovate. With Google, the restructuring of different goals throughout the Alphabet umbrella, and with Amazon, through its small starting teams on new initiatives.
Not only are these companies structured in this way, but the culture promotes and encourages innovation. Through hackathons, structured time away from core duties, collaborative office environments that encourage discussion, and more, these organizations produce environments that are conducive to new ideas.
Open Executive Communication and Welcoming New Ideas
New ideas that come from within an organization must be encouraged by executives to flourish. They must be approved from the top-down, but often are sparked from the bottom-up, according to an article in Forbes on innovation in the workplace.
But not only that, most innovative organizations welcome ideas from outside perspectives and divergent disciplines. Cross-functional teams of individuals in different roles can help encourage new ideas or even bring in outside resources to help foster creativity such as a consultant or freelancer. In Google’s case, it even brings in academics and researchers who spend sabbaticals within the organization. With this kind of encouraging collaboration happening daily, innovative ideas are born organically.
The CEO of YouTube, Susan Wojcicki said, “Some of the best ideas at Google are sparked just like that – when small groups of Googlers take a break on a random afternoon and start talking about things that excite them.”
Trust Employees and Give them Freedom

(Image Source/Dan Pink pictured)
A logical step from creating a culture of innovation and executive buy-in is, of course, fully trusting your employees and giving them the freedom to do what they do best. The best example of this is of course Google’s 20% time, but there are many others.
In one of the most popular TED talks, career analyst Dan Pink said that the three main drivers of motivation are:
- Autonomy
- Mastery
- Purpose
Give employees autonomy, allow them to do what they are most competent in, and give them purpose. Success and innovation will follow naturally with that recipe.
Move Fast
One of the most common themes in all these organizations is they are not afraid to fail, aim for big ideas, and move fast. They start new ideas with small groups, and as the idea grows it spreads to the rest of the organization. As innovation consultant, Tendayi Viki said in Forbes “As we succeed with early adopters, other business leaders will then be attracted to our transformation agenda.”
Embrace Failure
Companies cannot be the most innovative in the world, creating products that have never been thought of before, without the reality that failure will occur. But by thinking of failing fast as a core competency and a success, not a mistake, organizations can move past these inevitable roadblocks. “Failure is the way to be innovative and successful. You can fail with pride,” says Google’s chief social evangelist Gopi Kallayil.
Have a Higher Purpose

Perhaps most important of all is to have a higher purpose. An organization that does not have a north star that drives all business actions and eliminates distracting elements will not be able to consistently perform at a high level. One of the most innovative business leaders of all time, Steve Jobs, said it best, “Innovation is saying no to a thousand things.”
And in his Stanford commencement speech, he said, “Your work is going to fill a large part of your life, and the only way to be truly satisfied is to do what you believe is great work. And the only way to do great work is to love what you do.”
The greatest organizations may have lots of products and services that are seemingly unrelated, but they all follow a singular mission. And as organizations grow, and hire people who believe in this purpose, it only gets stronger and more meaningful. Whether it’s “To organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful” like Google, or “To give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together,” like Facebook, these ambitious goals drive the world’s most innovative organizations. And with this blueprint, it can drive yours as well.
Learn MoreCABEM’s Competency Management Software
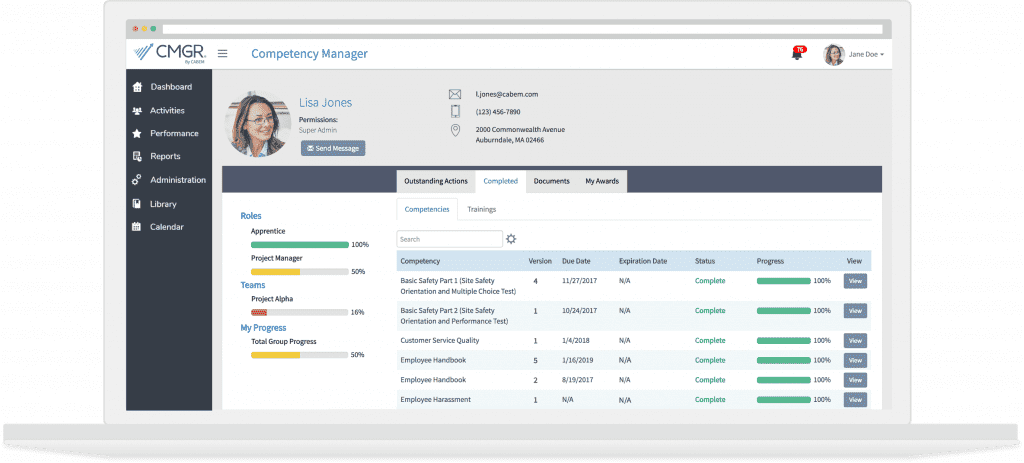
In order to succeed and innovate like a FANG company, you must run your organization and train your employees in an innovative way. While many companies train using Learning Management Systems (LMS) or using documents and spreadsheets, these are outdated and incomplete methods.
Competency management software such as our own Competency Manager allows companies to formally build competency programs and deliver them to all individuals and locations across the organization. This allows them to not only train individuals, but to prove that the training is successful, and track progress and/or required credentials.
Click to learn more about our Competency Management Software, or contact us to schedule an introductory call today!

