The manufacturing industry has come around to realizing the power of competency-based training philosophy, and is seeing benefits in reduction of injuries, efficiency, and performance as a result. Find out below what competency management and modeling is, and how to implement this type of approach to benefit your learning and development and safety programs.
What is a Competency Model?
A competency model is “a collection of multiple competencies that together define successful performance in an established work setting” according to Competency Model Clearinghouse. It provides a description of what an individual needs to know and be able to do within their job role. This can include specific job-related skills, but also knowledge, behaviors, and abilities as it pertains to the organization or the industry as a whole.
What is the Competency Model Clearinghouse?
The Competency Model Clearinghouse (CMC) is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration (ETA). The goal of the Clearinghouse is to inform the public workforce system about the value, development, and uses of competency models. The Competency Model Clearinghouse has an initiative called the Industry Competency Model Initiative, in which they are developing dynamic models of competencies for a variety of different industries. If you are unfamiliar with competency development and need a good place to start, I suggest you check out the website after reading this article to see what information it has that pertains to your organization.
Motorcycle Manufacturer Case Study
Within manufacturing, different models have been developed to cater to a category of expertise. The Tooling U-SME Competency Framework outlines specific competencies for each job role in nine functional areas, including Machining, as described in the case study below.
How can a competency model system improve manufacturing? Consider the case of the North American motorcycle manufacturer, cited in this report below by Tooling-U, “Using Competency Models to Drive Competitiveness and Combat the Manufacturing Skills Gap.”
In this example, the manufacturer wanted to develop technical employees into workers who could perform in a broader spectrum of roles across the globe. According to the report, “The team developed a competency framework and designed curriculum elements to include a standardized blended program of online classroom, simulated work and on-the-job training (OJT).”
The report states, “The use of a competency framework resulted in an accelerated process, with workers achieving competency 60 percent faster than with standard training programs, resulting in productivity gains and cost savings.”
Tooling U-SME Case Study
Tooling U-SME is a workforce development provider of online learning solutions. It offers a wide range of online classes, instructor-led, and blended learning.
If Tooling U-SME can be combined with an automated system for competency management, the results will be a more extensive dissemination of the competencies and trainings, easier access by companies and individuals, and a more efficient system for tracking individual progress. Besides this specific case study related to a motorcycle manufacturer, it is clear that other companies can benefit from the use of the competency model described.
Advanced Manufacturing Competency Model
The Advanced Manufacturing Competency Model (below) from the Manufacturing Institute, was developed by manufacturers to illustrate the competencies and skills needed by workers in the industry, whether just starting out or looking to progress in their career. It includes core skills and competencies such as:
- Personal effectiveness
- Workplace competencies
- Basic applied skills in reading, writing, math, and locating information
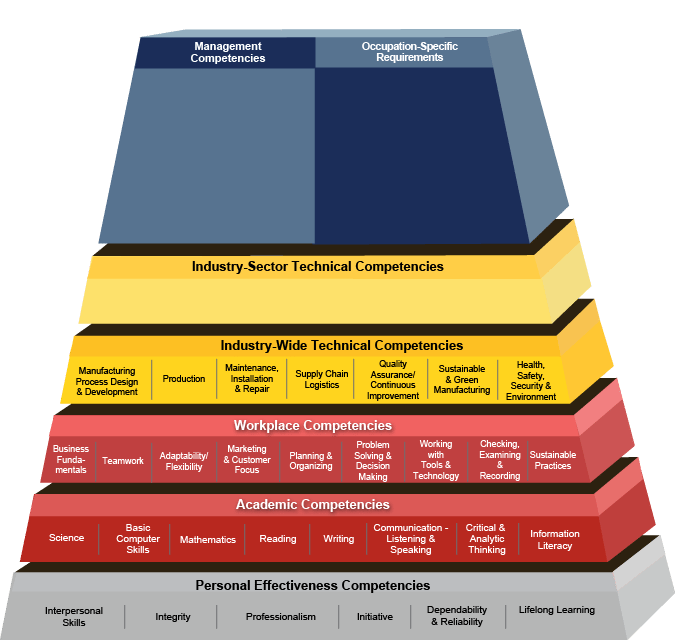
Next are the critical industry-wide technical competencies. These are crucial for safety and quality programs and will be different based on the industry. These types of competencies can be completed by a blended learning program that includes test taking, on the job training (OJT), instructor led training (ILT), and more. This is accomplished easier using a competency management software system than using online communication such as email or Microsoft Office, and also is preferable over traditional LMS.
The third level of certification is specific to the sector of an industry. Occupations that are in demand are matched with industry certifications, examples include welding, fabrication, and more.
At the top of the Competency Model are managerial and specialty occupations, which can be covered with certifications and advanced degrees.
The Advanced Manufacturing Competency Model is an effort on the part of manufacturers to develop a common reference of skills necessary to succeed in a variety of professions but will be different and specific to each company and industry within manufacturing. The model was updated in 2010 to reflect new information about sustainable and environmentally-friendly manufacturing behaviors.
Competency Models in Action – Competency Based Education
Competency Based Training can apply to a variety of different industries. In the below case study, the National Center for Biotechnology Workforce collaborated with the Los Angeles Valley College to develop the Biotech Bridge Training program, which helped build a pipeline of talent.
The organization developed a “a six-week program designed to help students develop a much-needed set of core skills and competencies targeted specifically for the bioscience industry.” The program is very selective, only choosing 20-30 students. From the program, students learned hard skills in math and science as well as soft skills such as interview and preparation.
A global pharmaceutical company, Baxalta, has hired 96 students from this program, with only a 5% turnover. Average turnover of employees hired via HR and normal onboarding procedures is 23% according to the study. Another company Grifols, a global biopharmaceutical manufacturing company, has hired 25 students from this program. This program proves that when care and attention are taken to train manufacturing employees to a set of core competencies, it produces excellent workers. To learn more on how to implement this in your own organization, read our article on How to Apply Competency-Based Methodology to Learning and Development Programs.
Conclusion
It is clear that some manufacturers are already developing competency models for various categories in their industry and benefiting from them. However, most manufacturers are still relying on online learning or classroom teaching to improve their workers’ skills. In this era of advanced technology, these methods are outdated, costly, and limited.
If manufacturers can advance to an automated system for competency management they will see many benefits:
- A system that adapts to manufacturing companies’ changing needs
- A variety of training methods that cater to individual learning preferences, whether written, visual, OTJ, ILT, blended, and more.
- Wider distribution of competency model management within the manufacturing workforce as a whole, and within individual companies.
- Ease of access from all employees via computers
- Easier storage of data to mark progress and keep track of credentials, and for supervisors to keep track of employees’ training
Manufacturing is a rapidly changing industry, and to account for these changes, companies would benefit greatly from modernizing their workforce development programs with competency management. Our Competency Manager software is designed to help manufacturers build a framework for individual competency. To learn more and request a demo, click here.
Other articles that may interest you:
Competency Modeling for Beginners: What it is and How You Can Do It Too!

